Posted November 17, 2023
By Ray Blanco
Quantum-Powered Healthcare
Artificial intelligence is quickly transforming just about every industry that exists. Nearly every job imaginable can at least be assisted by the wide array of publicly available AI tools.
Even baseball pitchers are throwing faster than ever before thanks to AI.
But the industry that seems to be benefitting more than any other is biotech.
I recently covered how AI is breathing life back into the research and development of new drugs, something that over the years has taken longer, cost more, and produced less.
It makes sense that AI would be so universally beneficial, while also being an exceptional boon to biotech. It’s because when it all boils down to it, AI is nothing more than the next evolution of possibly the most valuable practice in human history…
Data analytics.
The advanced practice of learning from past events is highly valued across all fields, and AI takes that to the next level.
The Large Language Models that generative AI programs are built on top of are “only” enormous collections of data, which is then used to identify patterns and, in some cases, make projections and predictions.
There really shouldn’t be anything surprising about AI being so helpful to R&D, considering its extremely data-driven nature.
AI is changing the world. You know that already.
But the less talked about, more niche, but every bit as powerful and transformative technology of quantum computing is also proving to be extremely useful in driving biotech into the future.
Quantum computing, which uses multi-state qubits as opposed to the binary bits of traditional computing, is an extremely powerful form of computing that until now has been a tough knot to untangle.
With the recent advances in quantum computing, the question of its practical utility has been brought up frequently.
The most discussed use for quantum computing is encryption and decryption, due to its potential to solve incredibly complicated equations that would take traditional computers years to complete.
But a recent partnership between IBM and Moderna aims to use this powerful technology to advance their therapeutics to levels never before reached.
A New Era Of Medicine
This new partnership hopes to harness the power of both quantum computing as well as AI to improve all of its life sciences, but in particular its mRNA designs.
They will utilize an AI model called MoLFormer to make predictions about and gain insight to potential mRNA treatments. The model will be used to optimize lipid nanoparticles as well as the mRNA itself, which will greatly help the durability and effectiveness of future medicines.
Moderna will be utilizing IBM’s Quantum Network and participate in their Quantum Accelerator program.
How can quantum computing be used to further drug research?
One company that’s already using small-scale quantum computing to do so is POLARISqb.
Founded in 2020, POLARISqb has used quantum computing to improve computer-aided drug design (CADD), which is a critical part of the R&D process as it allows researchers to predict the effects of potential treatments before ever even entering a lab.
CADD is a slow and limited process using traditional computing, with only a few compounds being able to be tested at any given time.
While traditional CADD runs every possibility, brute-forcing a solution, POLARISqb utilizes a “quantum annealer” to solve the complicated optimization problems that would have previously been impossible.
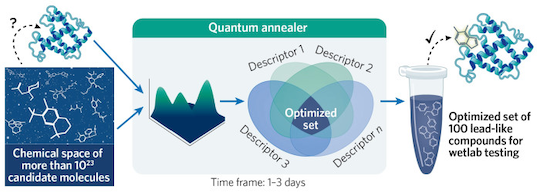
POLARISqb has already proven the effectiveness of this new method, building a chemical library of 1.3 billion compounds and using the quantum annealer to design molecular leads. Within six months they were able to prioritize thirty lead molecules, ten of which shared similar motifs to molecules that took years to identify.
With the combination of artificial intelligence and quantum computing being used to jumpstart a slumping drug development industry, the new treatments and improvement to existing treatments should improve exponentially.

